Documentation
RINGO: RINEX pre-processing tool using Go!⌗
RINGO is a RINEX pre-processing tool capable of handling multi-GNSS data. The software is a command line based CLI tool that works on various platforms including Windows OS, macOS, Linux, Unix.
RINGO’s command line interface (CLI) is simple to use, but fully featured to manage daily GNSS data observed by a Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) network.
Table of Contents⌗
- Features
- Installation
- Supported Platforms
- Basic Usage
- Command References
- merge – Merging, editing, and version conversion etc.
- qc – Quality check
- clkcorr – Clock jump correction
- ioncorr – Ionospheric correction
- viewer – Generation of interactive viewer
- rnxcsv – Csv conversion of RINEX observation data and QC result
- bingo – Conversion of BINEX to RINEX files
- rtcmgo – Conversion of RTCM to RINEX files
- completion – Generation of a shell completion script
- cal – Show GNSS calendar
Features⌗
- RINEX file editing ("merge")
- RINEX file merging ("merge")
- Clock jump correction ("clkcorr")
- Quality check ("qc")
- Ionospheric correction ("ioncorr")
- Generation of interactive viewer ("viewer")
- Csv outputs of RINEX observation data or Quality check result("rnxcsv")
- Conversion of BINEX and RTCM binaries to RINEX files ("bingo", “rtcmgo”)
- Generation of a shell completion script ("completion")
- GNSS calendar display ("cal")
Installation⌗
Prebuilt binaries for various platforms are available on this website.
- Download the latest release of the RINGO software from the download page
- Copy the binary executable suitable to your operating system to your desired directory
- Add the directory to the PATH environment variable
- Add the permission to the installed executable, i.e.:
$ chmod +x ringo
Supported Platforms⌗
Currently supports Windows OS, macOS, Linux, UNIX (FreeBSD, Solaris).
Supported formats⌗
| file format | version |
|---|---|
| RINEX | 2.00*, 2.10, 2.11, 2.12 |
| 3.00, 3.01, 3.02, 3.03, 3.04, 3.05 | |
| 4.00, 4.01, 4.02 |
* Currently official RINEX version 2.00 document is not available from IGS, so RINGO support for RINEX version 2.00 may not be maintained.
Supported formats for data conversion:⌗
| file format | record types |
|---|---|
| BINEX | 0x7f: GNSS observables |
| 0x01-0x01: GPS ephemeris | |
| 0x01-0x02: GLO ephemeris | |
| 0x01-0x03: SBAS ephemeris | |
| 0x01-0x06: QZS ephemeris | |
| 0x01-0x14: GAL ephemeris |
| file format | record types |
|---|---|
| RTCM | MSM7 (1077, 1087, 1097, 1117): GNSS observation data |
| 1019: GPS ephemeris | |
| 1020: GLO ephemeris | |
| 1044: QZS ephemeris | |
| 1046: GAL ephemeris |
Basic usage⌗
Test installation⌗
You can test your installation by version command:
$ ringo
Then you will see like:
$ ringo
RINEX file pre-processing tool using Go.
ringo is a program for editing, pre-processing, and quality checking RINEX files,
also includes features such as conversion from BINEX or RTCM to RINEX format, interactive viewer etc.
Interface⌗
RINGO is a CLI tool that provides several sub-commands. Basic interface is as follows:
$ ringo [sub-command] [flags] inputfiles > outputfile
RINGO reads all inputfiles that are given in arguments, and print data to the standard output. The basic usage is to specify input files as command line arguments and redirect it to an output file.
$ ringo merge rinex1 rinex2 > rinex_merged
or you can use the option “-o” to specify the output file as a command line argument.
$ ringo merge rinex1 rinex2 -o rinex_merged
See the help for each sub-command to see the full set of options available.
Input file⌗
The inputfiles can be any of RINEX observation file, RINEX navigation file, IGS IONEX file. The file format is automatically identified from the file header.
The direct reading of compressed file is also supported. Acceptable formats are “compress (.Z)”, “zip (.zip)”, “gzip (.gz)”, “bzip2 (.bz2)” for all file format, and tar archived navigation file is also supported.
Furthermore, hatanaka compressed file can also be accepted.
For example:
$ ringo merge rinex_obs1.o rinex_obs2.o.gz > rinex_merged // compressed file
$ ringo merge rinex_obs1.o rinex_obs2.d > rinex_merged // hatanaka compressed file
$ ringo merge rinex_nav.tar.bz2 > rinex_nav.p // tar archived navigation file
* The previous ringo v0.8.5 requires “CRX2RNX” command to be available in PATH to extract hatanaka compressed files, but starting with ringo v0.9.0, direct reading has been supported. Note that this feature depends on crinex library.
Show commands available⌗
$ ringo help
shows
.....
Usage:
ringo [command]
Available Commands:
bingo Convert a BINEX file to RINEX files
cal Displays a GNSS calendar
clkcorr Correct obs rinex by timetag smoothing
completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
genconf Generate a default conf file
help Help about any command
ioncorr Correct ionospheric delay of rinex obs file
merge Merge observation or navigation RINEX files
qc Quality check of a rinex obs file
rnxcsv Convert RINEX files to csv format
rtcmgo Convert a RTCM3 file to RINEX files
version Show version
viewer Generate a HTML5-based viewer
.....
Use "ringo [command] --help" for more information about a command.
The helps for each sub-command can also be also displayed by:
$ ringo [command] --help
For example,
$ ringo bingo --help
Convert a BINEX file to RINEX files
Currently supports 0x01 ephemerides and 0x7f-05 observations.
Example:
convert a BINEX file to RINEX obs and nav files.
>> ringo bingo --outobs rinexobs --outnav rinexnav binex
.....
Command references⌗
ringo⌗
ringo is the main command of the RINGO software, and each sub-command is invoked by passing the command in the first argument. There are two types of flags: global flags and command options. The global flags are commonly used for all sub-commands, and the command options are defined for each-command.
global flags⌗
| Flag | Shorthand | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --config | use a config file (default is $HOME/.ringo.yaml) | |
| --debug | enable debug print to stderr [default: false] | |
| --help | -h | show help for ringo |
| --elmaskf | elmask angle (const; degrees) or file (for azimuth-dependent elmask) [default: ‘’] | |
| --etime | -e | end of time window (e.g. ‘2017/01/01 15:00:00’) (default “2099/12/31 23:59:59”) |
| --stime | -s | start of time window (e.g. ‘2017/01/01 03:00:00’) (default “1980/01/06 00:00:00”) |
| --exclPRN | list of PRN to exclude (e.g. ‘G01,G02’) [default: ‘’] | |
| --exclSat | list of satsys to exclude (e.g. ‘G’, ‘REJ’) [default: ‘’] | |
| --inclPRN | list of PRN to include (e.g. ‘G01,G02’) [default: ‘’] | |
| --inclSat | list of satsys to include (e.g. ‘G’, ‘REJ’) [default: ‘’] | |
| --interval | time interval to output (seconds) | |
| --outfile | -o | output file [default: STDOUT] |
| --outver | RINEX version to output, e.g., ‘4.00’ | |
| --sort | sort timetag and PRN [default: false] | |
| --ignore-skipped-lli | ignore skipped LLI flags by the interval change [default: false] | |
| --seconds-keep-lli | seconds to keep skipped LLI flags (seconds) [default: 3600]. If data is thinned out with the “--interval” option, the LLI flag of the data is held for the duration specified here and is set for the next output. |
|
| --toggle | -t | help message for toggle |
| --verbose | -v | enable verbose print to stderr [default: false] |
| --version | show version for ringo |
merge⌗
merge merges and edits RINEX observation and navigation files. It offers basic editing features for RINEX files, including clipping, sorting, editing header, change of observation types.
The header contents of the merged file basically follow the header contents of the first file appeared in the argument. However, some header contents are automatically modified according to the contents of the merged file.
The header contents listed below are modified after merge multiple files.
| Header label | Description |
|---|---|
| VERSION | The output version will be the same as the version of the first file unless you choose otherwise in the option |
| TIME OF FIRST OBS | automatically modified according to the data period of the merged file |
| TIME OF LAST OBS | automatically modified according to the data period of the merged file. Note that the “TIME OF LAST OBS” is an optional, but RINGO always outputs this header. |
| INTERVAL | automatically modified according to the data interval. Currently RINGO determines the interval as the most frequently occurred time interval in the merged file. |
| # / TYPES OF OBSERV | The obstypes will change according to the contents of the file contents after the merge. |
| SYS / # / OBS TYPES | Same as the “# / TYPES OF OBSERV” |
options⌗
| Flag | Shorthand | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --obstypes | -t | mask of obscodes (e.g. ‘C1C,L1C,L2X&R:S1C,C1P&E:L5X’) [default: ‘’] |
| --deepMerge | deeply merge RINEX observation files including PRN, obstypes within overlapping timetags [default: false] (TO BE DEFAULT FROM v0.9.2) | |
| --phaseshift | apply phase shift correction | |
| --help | -h | show help for merge |
| --h.add-new-record | add new optional headers if possible | |
| --h.agency string | set agency | |
| --h.ante string | set antenna dE | |
| --h.anth string | set antenna dH | |
| --h.antn string | set antenna dN | |
| --h.antnum string | set antenna number | |
| --h.anttype string | set antenna type | |
| --h.aprx string | set approximate pos x | |
| --h.apry string | set approximate pos y | |
| --h.aprz string | set approximate pos z | |
| --h.doi string | set DOI for data citation | |
| --h.license string | set License (separator ‘;’ for multiple lines) | |
| --h.mname string | set monument name | |
| --h.mtype string | set monument type | |
| --h.no-inpfiles | do not show input files in the header | |
| --h.observer string | set observer | |
| --h.recnum string | set receiver number | |
| --h.rectype string | set receiver type | |
| --h.recver string | set receiver version | |
| --h.stainfo string | set Station Information (’;’ for multiple lines) |
Examples⌗
Merge & Edit⌗
File merge
$ ringo merge 02550010.21o 02550020.21o > 02550010_merged.21o
$ ringo merge 025500[12]0.21o > 02550010_merged.21o
Extraction of compressed file is possible.
$ ringo merge 02550010.21o.gz > 02550010.21o
$ ringo merge 02550010.21o.bz2 > 02550010.21o
Hatanaka compressed file can also be extracted directly.
$ ringo merge 02550010.21d.gz > 02550010.21o
Creation of merged navigation file
$ ringo merge ????0010.21n > merg0010.21n
Merge of tar archived navigation file provided by GSI
$ ringo merge 02550010.21N.tar.gz > 02550010.21p
Header Edit⌗
Set header to the file
$ ringo merge 02550010.21d.gz --h.agency GSI --h.observer Kawamoto > 02550010.21o
Clipping⌗
Clip the data between “2021/01/01 01:00:00” and “2021/01/01 02:00:00”
$ ringo merge --stime "2021/01/01 01:00:00" --etime "2021/01/01 02:00:00" 02550010.21o > 02550010_clip.21o
Crop the data of L1 and L2 only.
The observation types can be specified by a comma separated string.
$ ringo merge --obstypes "L1,L2" 02550010.21o > 02550010_l1l2.21o
Clipping to the L1C data only, but only GPS clipping to L2X and L5X.
The observation types can be set for each satellite system individually. The setting for each satellite system can be specified by starting one of the character “GRJECS”. The settings can be combined with “&”.
$ ringo merge --obstypes "L1C&G:L2X,L5X" 02550010.21o > 02550010_m.21o
Clip to data containing only specific satellite systems. The satellite systems can be a combination of “GRJECS”.
$ ringo merge --inclSat "G" 02550010.21o > 02550010_G.21o # GPS only file
$ ringo merge --inclSat "GJ" 02550010.21o > 02550010_GJ.21o # GPS and QZSS
$ ringo merge --exclSat "G" 02550010.21o > 02550010_noGPS.21o # no GPS
Clip to data containing only specific satellites. The satellites can be a comma separated string with viecle IDs.
$ ringo merge --inclPRN "G01,G02" 02550010.21o > 02550010_G01G02.21o # only G01 and G02
$ ringo merge --exclPRN "G01,G02" 02550010.21o > 02550010_G01G02.21o # without G01 and G02
Change the data interval by thinning out the data. The data interval can be set in seconds.
$ ringo merge --interval 60 02550010.21o > 02550010_60s.21o
Sorting⌗
Sorting of the data is also possible
$ ringo merge --sort 02550010.21o > 02550010_sorted.21o
Then the sorted file looks like:
> 2021 01 01 00 00 0.0000000 0 31
G05 21697284.266 114019997.871 7 -2085.000 46.700 21697290.6094 88846772.50546 -1624.6764
G13 20934053.969 110009159.077 8 -1751.844 49.100 20934059.5314 85721462.52546 -1365.0704
G14 24505154.219 128775502.796 6 613.117 39.200 24505160.5594 100344544.64143 477.7544
G15 20366192.609 107025043.761 8 544.027 51.300 20366198.4884 83396175.49049 423.9184
G18 21709562.883 114084519.671 7 1345.543 44.600 21709568.6414 88897037.58246 1048.4774
G20 23553429.875 123774104.162 6 3244.309 38.400 23553435.1254 96447392.24343 2528.0314
G23 23850618.016 125335843.457 6 3100.906 39.800 23850624.1374 97664324.07344 2416.2894
G24 21628936.797 113660828.469 7 3088.203 44.900 21628945.8284 88566938.42948 2406.3914
...
Elevation mask⌗
Elevation mask can be set by a constant angle (degrees). Specify navigation files for the second or subsequent input files. The navigation file is necessary to calculate the elevation angles.
$ ringo merge --elmaskf 30 02550010.21o 02550010.21n > 02550010_mask30deg.21o
$ ringo merge --elmaskf 30 02550010.21o 02550010.21N.tar.gz > 02550010_mask30deg.21o
Elevation mask that changes depending on azimuth angle can be also specified by a mask file:
$ ringo merge --elmaskf elmask.txt 02550010.21o 02550010.21N.tar.gz > 02550010_mask.21o
Here, the elevation mask file (elmask.txt) is looks like:
% Elevation Mask
% AZ(deg) EL(deg)
0.0 7.4
1.0 7.2
2.0 9.4
3.0 10.2
...
And this is an example of the azimuth-dependent elevation mask:
| skyplot | |
|---|---|
| original | 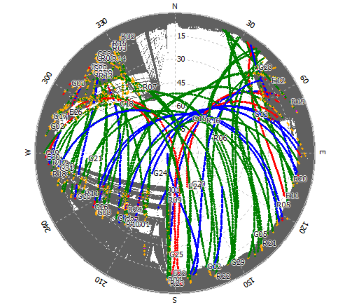 |
| masked | 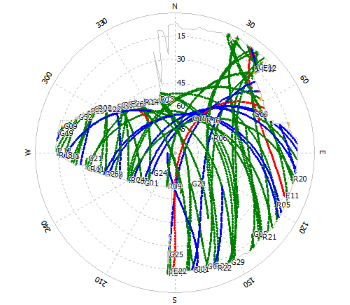 |
qc⌗
qc checks the quality of RINEX observation file. It summarizes the total number of epochs, the number of obsevation data, number of observations for each signal, multipath noise, cycle slips, etc.
Examples⌗
$ ringo qc 02550010.21o 02550010.21n > qc.log
$ ringo qc 02550010.21d.gz 02550010.21N.tar.gz > qc.log
clkcorr⌗
clkcorr corrects clock jump events in RINEX files. In default, the output file is aligned to regulary spaced timetags by correcting clock jumps. This behavior is similar to the “-smtt” by the teqc software. Optionally the output file can be switched to a smoothed range data. Then the msec clock jumps could be accumulated on the timetags.
Examples⌗
$ ringo clkcorr XXXXXXXX.XXo > timetagsmoothed_RINEX
$ ringo clkcorr --smpr XXXXXXXX.XXo > rangesmoothed_RINEX
ioncorr⌗
ioncorr corrects ionospheric effects on GNSS signals. The 1st- and 2nd-orders of ionospheric corrections are implemented in RINGO ioncorr. The correction requires IONEX file provided by IGS as well as navigation files.
Examples⌗
// remove the 1st order effect
$ ringo ioncorr -1 02550010.21o 02550010.21N.tar.gz igsg0010.21i > 02550010_1.21o
// remove both the 1st and 2nd order effects
$ ringo ioncorr -1 -2 02550010.21o 02550010.21N.tar.gz igsg0010.21i > 02550010_12.21o
viewer⌗
viewer generates a HTML5-based interactive viewer for RINEX observation file and quality check result.
Examples⌗
$ ringo viewer 02550010.21o > 02550010_21o.html
$ ringo viewer --qcmode 02550010.21o > 02550010_21o_qc.html
rnxcsv⌗
rnxcsv converts a RINEX file to CSV format divided by each observation code.
Examples⌗
// output a csv file containing all satellites
$ ringo rnxcsv obsfile > rnx.csv
// output csv files to an output directory and csv files are output separetely for each satellite
$ ringo rnxcsv obsfile --outdir ./out
// output a csv file that also includes azimuth and elevation angles by additional navigatin file
$ ringo rnxcsv obsfile navfile > rnx.csv
Then the output file looks like:
> PRN, time, az, el, C1C, L1C, D1C, S1C, C2W, L2W, D2W, S2W, C2X, L2X, D2X, S2X, C5X, L5X, D5X, S5X
G01, 2021-01-01 11:04:30.000, 196.84, 5.70, 24885503.563, 130773983.465, 4048.820, 30.700, , , , , , , , , , , ,
G01, 2021-01-01 11:05:00.000, 196.84, 5.90, 24862386.023, 130652698.591, 4050.078, 31.300, 24862396.988, 101807359.859, 3155.906, 25.100, 24862396.621, 101807311.887, 3155.906, 34.800, 24862392.668, 97565339.833, 3024.410, 41.100
G01, 2021-01-01 11:05:30.000, 196.84, 6.11, 24839260.133, 130531173.631, 4051.367, 32.900, 24839271.230, 101712665.530, 3156.910, 27.100, 24839271.102, 101712617.554, 3156.910, 36.100, 24839266.750, 97474591.196, 3025.371, 40.900
G01, 2021-01-01 11:06:00.000, 196.83, 6.31, 24816128.070, 130409613.174, 4052.227, 33.200, 24816139.004, 101617943.573, 3157.578, 28.300, 24816138.402, 101617895.580, 3157.578, 36.400, 24816133.836, 97383816.091, 3026.012, 41.600
G01, 2021-01-01 11:06:30.000, 196.83, 6.52, 24792989.375, 130288019.850, 4053.562, 33.000, 24793000.121, 101523195.994, 3158.621, 28.300, 24792999.586, 101523148.008, 3158.621, 37.200, 24792994.977, 97293016.432, 3027.012, 42.000
...
“rnxcsv” also supports output of quality check result with the “--qcmode” option.
// output quality check results to a csv file
$ ringo rnxcsv obsfile navfile --qcmode > rnx.csv
The output file looks like:
> PRN, time, az, el, MP1, MP2, MP5, GF, MW, IOD1, s1, s2, s5, sg, sm, si
G01, 2021-01-01 11:05:00.000, 196.84, 5.90, 0.524, 0.150, 0.093, -15.203, -62.609, -38.704, , , , , ,
G01, 2021-01-01 11:05:30.000, 196.84, 6.11, 0.401, 0.268, 0.074, -15.312, -62.591, -38.981, , , , , ,
G01, 2021-01-01 11:06:00.000, 196.83, 6.31, 0.884, 0.704, -0.151, -15.429, -63.054, -39.277, , , , , *,
G01, 2021-01-01 11:06:30.000, 196.83, 6.52, 0.981, 0.727, -0.076, -15.542, -63.118, -39.567, , , , , ,
...
Asterisk “*” indicates the timing at which a cycle slip is detected from the linear combination. Slips on MP1 (s1), MP2 (s2), MP5 (s5), GF (sg), MW (sm), and IOD (si) are shown.
bingo⌗
bingo converts a BINEX file to RINEX observation and navigation files.
Examples⌗
$ ringo bingo 02550010_21.bnx --outobs 02550010.21o --outnav 02550010.21p
rtcmgo⌗
rtcmgo converts a RTCM file to RINEX observation and navigation files.
Examples⌗
$ ringo rtcmgo 02550010_21.rtcm --outobs 02550010.21o --outnav 02550010.21p
completion⌗
completion outputs shell completion scripts for bash, fish, powershell, and zsh. These scripts enable the tab auto-completion when ringo command is typed in the terminal, and automatically fills in partially typed command and flags when tab key is pressed.
The following command outputs the shell completion script for ringo:
$ ringo completion [ bash | fish | powershell | zsh ] > completion
Note that currently this feature depends on cobra library.
Examples⌗
If you want to enable shell completion, firstly output the completion script as:
$ ringo completion bash > completion.bash
Then you can enable the completion for ringo command by adding following line in .bashrc etc.
$ source completion.bash
The completion example is shown below.
$ ringo merge --h.[tab]
--h.add-new-record (add new optional headers if possible)
--h.agency (set agency)
--h.ante (set antenna dE)
--h.anth (set antenna dH)
--h.antn (set antenna dN)
--h.antnum (set antenna number)
--h.anttype (set antenna type)
--h.aprx (set approximate pos x)
--h.apry (set approximate pos y)
--h.aprz (set approximate pos z)
--h.doi (set DOI for data citation)
--h.license (set License (separator ';' for multiple lines))
--h.mname (set monument name)
--h.mtype (set monument type)
--h.no-inpfiles (do not show input files in the header)
--h.observer (set observer)
--h.recnum (set receiver number)
--h.rectype (set receiver type)
--h.recver (set receiver version)
--h.stainfo (set Station Information (';' for multiple lines))
You can see examples of settings for use in other shells in completion command’s help.
$ ringo completion --help
cal⌗
cal displays a GNSS calendar of a given month and/or year. In addition to the normal calendar, this calendar also displays GNSS week and DOY.
For default, cal displays only the current month. If month or year is given, it prints the calendar of specified month / year. In the case only the year is specified, a gnss calender for one year period is displayed.
Usage⌗
$ ringo cal [Flags] [[month] year]
flags:
-h, --help help for gnsscal
-n, --hoff turns off highlight of today [default: highlight on]
-3 three-month layout that displays previous, current and next months
--satsys satellite system of GNSS week; 'GPS', 'QZS', 'GAL', 'BDS', or 'GLO' [default: GPS]
Examples⌗
// Display the GNSS calendar for current month
$ ringo cal
GPS October 2023
Week Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat
2282 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
274 275 276 277 278 279 280
2283 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
281 282 283 284 285 286 287
2284 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
288 289 290 291 292 293 294
2285 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
295 296 297 298 299 300 301
2286 29 30 31
302 303 304
// Display the calendar for a specific month, e.g. January 2023
$ ringo cal 1 2023
GPS January 2023
Week Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat
2243 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
001 002 003 004 005 006 007
2244 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
008 009 010 011 012 013 014
2245 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
015 016 017 018 019 020 021
2246 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
022 023 024 025 026 027 028
2247 29 30 31
029 030 031